Evaluation of Water Supply Quality in Hanoi
2009 – 2020
Purpose of Program for Monitoring Hanoi Drinking Water
Community Service Project
- Provide information to the local and international community in Hanoi on drinking water safety.
- Determine Arsenic levels in Hanoi water supply
- Other parameters tested: nitrate, manganese, iron, hardness, total coliform, fecal coliform and free chlorine.
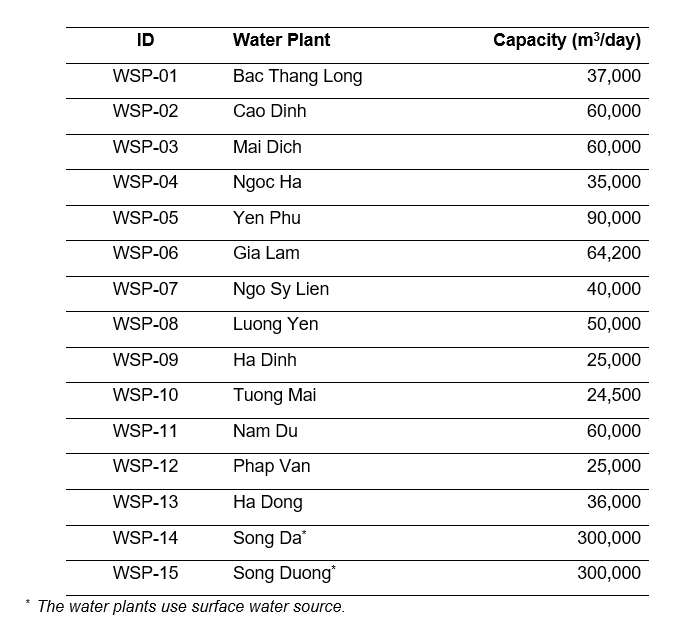
- Sampling sites: Households in the city nearby 13 main water supply treatment plants (WSPs) and 4 smaller water treatment stations
Arsenic Concerns
- Odorless and tasteless.
- Enters drinking water supplies from agricultural and industrial practices or natural deposits in the earth
- Arsenic has been linked to cancer of the bladder, lungs, skin, kidney, nasal passages, liver, and prostate (EPA, USA)
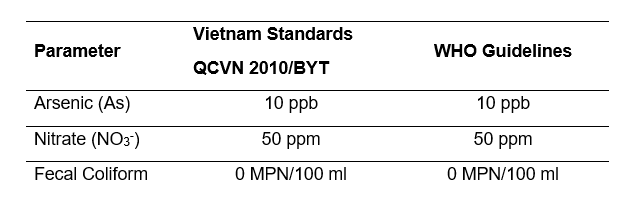
- National technical regulation on drinking water quality (QCVN 01:2009/BYT) and WHO standards allow maximum contaminant level (MCL) of 10 ppb for Arsenic
Table 1: Water plants for Hanoi’s water supply
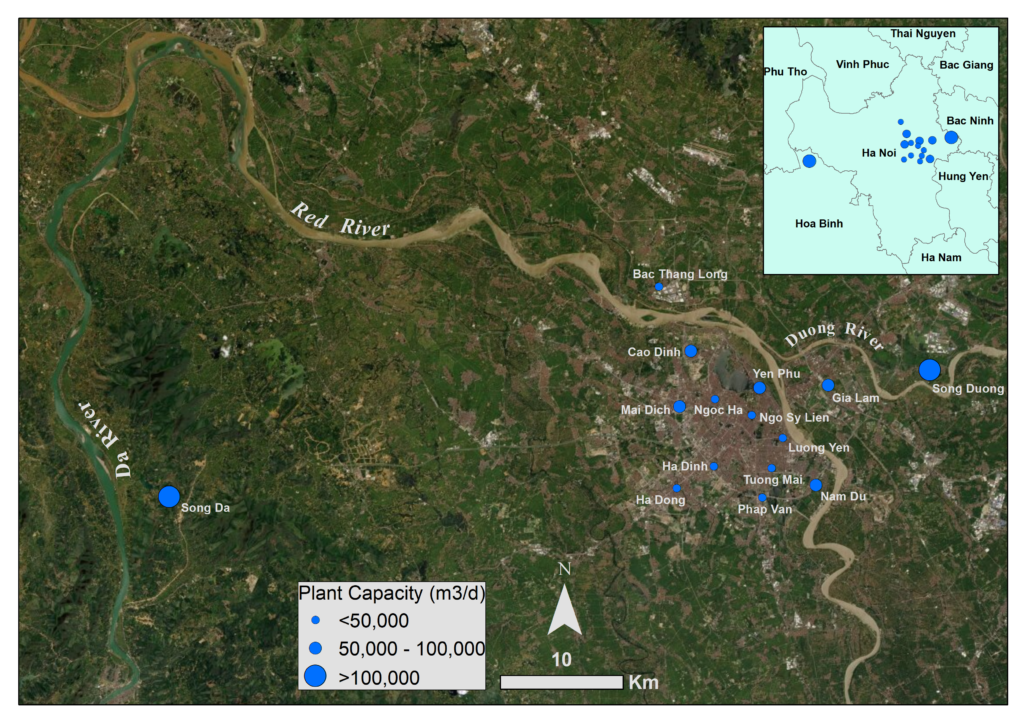
Figure 1: Map of water plants for Hanoi’s water supply
Field Program
- 32-35 water samples taken on each round
- Sample location description
- GPS location
- Field parameters tested
-
- Free chlorine
- Turbidity
- pH
- Temperature
-
Sample Handling
- Sample Collection
- 250 ml PE bottles are filled with water samples and stored and cooled by ice in a sealed container
- Samples delivered to the analytical laboratory within 8 hours
- Sample Acidification
- Samples for metallic parameters analysis are acidified with 3ml HNO3 solution
Laboratory Analysis
- Laboratory for Arsenic, other metals, and nitrate analysis:
- From May 2009 to December 2010: Institute Of Geological Sciences. Add: 84 Chua Lang Street, Dong Da, Hanoi.
- From December 2010 to February 2020: Department of Environmental Quality Analysis (DEQA) of Institute of Environmental Technology (IET) – Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST). Arsenic concentrations were measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma – Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
Testing Quality Assurance
- Chain of Custody:
- At the Institute a “Chain of Custody/Analytical Request Form” is filled in and signed by both the DS-Intl staff and the Lab staff
- Duplicates:
- Each round: duplicate samples account for 10% of total samples
- Blanks:
- One distilled water and three bottled water brands samples tested
- Matrix spikes for coliforms:
- Samples taken from the West Lake
Water Quality Standards
Table 2: Standards of some parameters for drinking water
Sampling Locations
- Sampling site selection criteria follows procedures:
- Tap water at households using treated water
- The closest residential place from the targeted water plant (normally not further than 1km)
- A few additional locations were selected to provide a broader coverage in the city
- Samples from the chosen locations were consistently sampled each quarter over the study period

Arsenic Analysis Result
- During the past 12 years of sampling (2009 to 2020), 12 sampling locations (accounting for 50% of the total 24 sampling locations) had average arsenic concentrations exceeding the standard (10 μg/L – WHO guideline).
- The average arsenic concentration at these 12 locations was 15.10 μg/L. Among these 12 sites, the H5 location had the lowest average arsenic level (5.10 μg/L), and the H16T location had the highest average arsenic level (28.30 μg/L).
- More recent results of the water sampling show that the arsenic concentration decreased in the last four years (from 2017 to 2020). Notably, in 2020 there is no water sample with arsenic concentration exceeding the standard. This can be explained by the fact that the two large-capacity surface water plants, Song Da Water Plant and Song Duong Water Plant, are now operating and providing water to Hanoi.
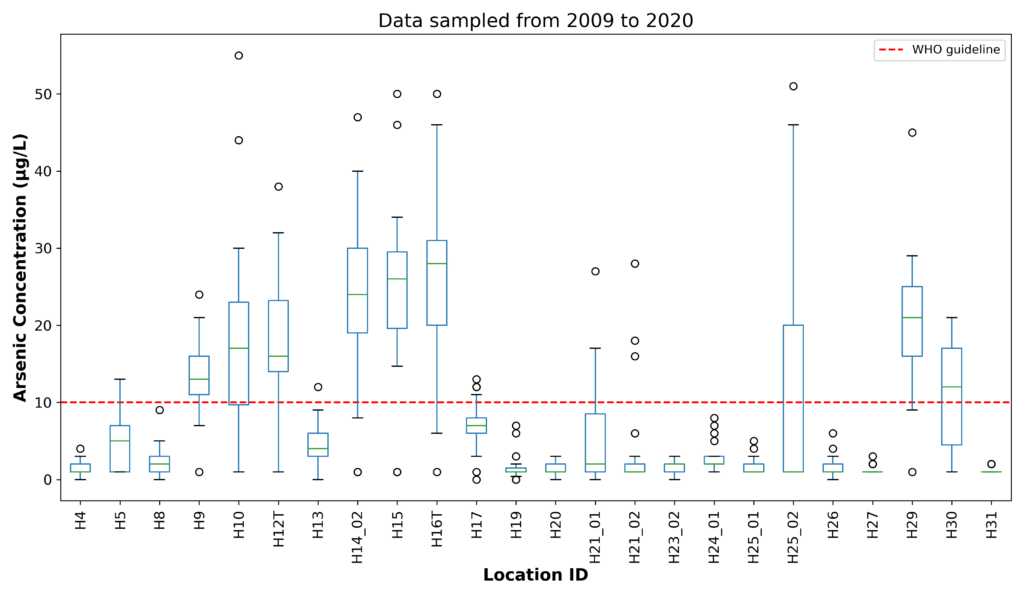
Figure 4: Arsenic concentration for sampling from 2009-2020
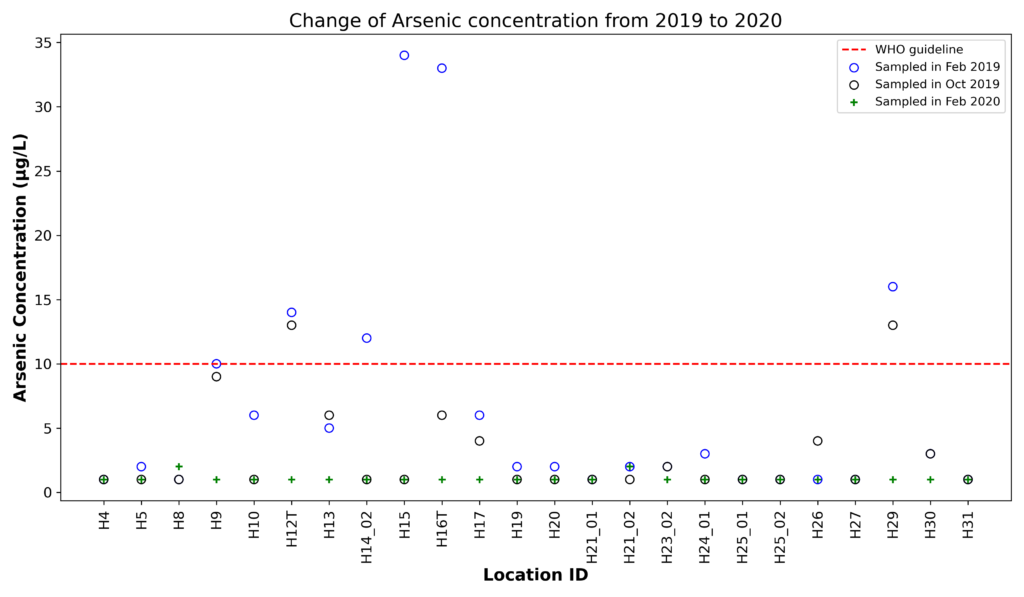
Figure 5: Arsenic concentration changed from 2019-2020